Intel Gaudi 3 Launch: AI Chip Set to Challenge NVIDIA's CUDA Dominance
In The News | 12-04-2024 | By Robin Mitchell
Key Things to Know:
- Challenging NVIDIA's Dominance: Intel introduces the Gaudi 3 AI accelerator, aiming to offer a robust alternative to NVIDIA’s GPUs, enhancing competition in the AI silicon market.
- Technological Advancements: Intel's Gaudi 3, crafted with TSMC's advanced 5-nanometer technology, offers substantial enhancements in performance, delivering 1835 TFLOPS of FP8 compute throughput.
- Market Dynamics: The introduction of Gaudi 3 by Intel may help reduce dependency on NVIDIA’s CUDA platform, providing engineers with more flexibility and potentially driving down costs due to increased competition.
- Promoting Open Standards: Intel emphasises open, community-based software and industry-standard networking with its new AI accelerator, aiming to democratize AI technology access and encourage innovation across various sectors.
With NVIDIA dominating the GPU and AI silicon market, many are concerned about the power that NVIDIA holds over the industry. In an effort to eliminate this challenge and to offer a viable alternative to NVIDIA's offerings, Intel has taken a significant step forward with the announcement of its Gaudi 3 AI accelerator, developed by Habana Labs, a subsidiary of Intel. This latest development underscores Intel's commitment to innovation in the AI space and aims to provide engineers with more options in AI hardware platforms.
What challenges does NVIDIA having a monopoly on AI hardware platforms introduce?
Over the past decade, developing AI algorithms has been an ongoing uphill battle. The first neural nets, simple in nature, could demonstrate the ability of AI to learn, but being simple, they could not be used for serious applications. To make them more complex, such nets need to add additional layers of processing and increase the total number of connections, but this quickly scaled up the amount of CPU resources.
Considering that CPUs are far from ideal for running AI neural nets, this introduced serious issues for engineers trying to develop ever increasingly more complex AI algorithms. Fortunately, researchers quickly found out that GPUs made ideal processing platforms for AI due to their ability to run thousands of complex polynomial equations simultaneously, which is essentially what neural nets are.
While there are numerous GPU manufacturers, one stood above the rest, NVIDIA. But for all the benefits that NVIDIA GPUs and the many developments around AI accelerators, there have been concerns regarding NVIDIAs position in the AI market, and its potential monopoly on the market.
The first challenge faced by engineers relates to the NVIDIA CUDA platform, the predominate method for running AI inferences and training. While CUDA itself has proved to be effective, the wide adoption of CUDA makes it challenging for engineers to shift away from NVIDIA alternatives.
Another issue faced is that NVIDIA's effective monopoly can lead to potential issues related to pricing and accessibility. With limited competition, NVIDIA may have more control over pricing, which could impact the affordability of AI hardware for researchers and companies. Additionally, a lack of alternatives to NVIDIA's hardware platforms may limit accessibility to AI computing resources, particularly for smaller organisations or researchers with budget constraints.
Furthermore, NVIDIA's dominance in the AI hardware market can create a barrier to entry for other companies looking to innovate and develop new AI technologies. The widespread adoption of NVIDIA's CUDA platform means that engineers and researchers may face challenges in transitioning to alternative platforms or developing new solutions that are not based on NVIDIA's technology.
Intel announces new AI silicon to combat NVIDIA
Recognising the challenges faced by AI developers, Intel recently announced the launch of a new device that it claims will help provide engineers with a new alternative to NVIDIA.
Intel's recent announcement of the Gaudi 3 AI accelerator, developed by its subsidiary Habana Labs, marks a significant leap in artificial intelligence computing. This third-generation processor is part of Intel's ongoing strategy to carve a niche in the burgeoning AI market, further bolstered by the acquisition of Habana Labs in 2019.
The Gaudi 3 accelerator, manufactured using TSMC's cutting-edge 5-nanometer process, showcases remarkable performance enhancements, setting a new benchmark in AI computing with 1835 TFLOPS of FP8 compute throughput. This technological leap signifies Intel's commitment to advancing AI accelerator capabilities. Smaller transistor sizes generally result in faster and more powerful chips, highlighting Intel's commitment to delivering high-performance AI computing solutions.
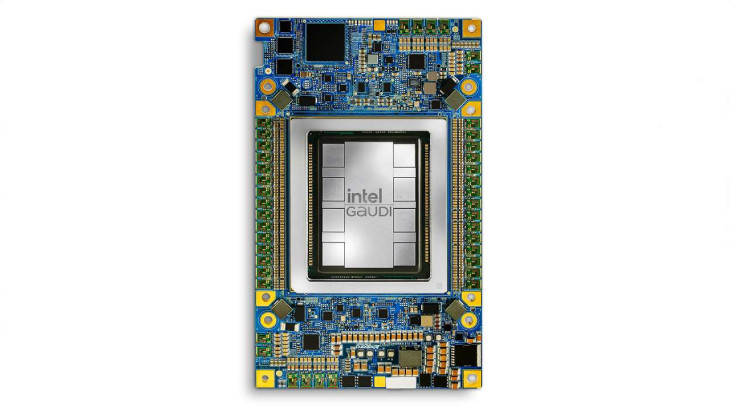

On April 9, 2024, at the Intel Vision event in Phoenix, Arizona, Intel unveiled the Intel Gaudi 3 AI accelerator. This new accelerator provides a fourfold increase in AI compute for BF16 and a 1.5 times boost in memory bandwidth relative to its previous model. (Credit: Intel Corporation)
Technological Advances
Intel's Gaudi 3 AI accelerator marks a considerable advancement in technological capabilities. Specifically, it delivers a 4x increase in AI compute performance for BF16 operations, a 1.5x increase in memory bandwidth, and doubles the networking bandwidth, which facilitates massive system scale-out compared to its predecessor, Gaudi 2. These enhancements not only demonstrate Intel’s drive to push the boundaries of AI hardware capabilities but also reflect their strategic focus on improving the efficiency and scalability of AI applications. Such progress ensures that Intel’s solutions are well-equipped to handle the demands of complex, large-scale AI models, further solidifying their position in the competitive AI market.
Market Positioning
Intel's introduction of the Gaudi 3 AI accelerator is not merely a technological upgrade but a strategic manoeuvre to cement its stance in a market heavily influenced by NVIDIA. By offering substantial improvements over previous generations and focusing on scalability and open standards, Intel positions the Gaudi 3 as a compelling alternative for enterprises looking to diversify their AI hardware portfolios. This strategic positioning is intended to challenge NVIDIA’s dominance and catalyze a shift in market dynamics, promoting greater competition and innovation within the AI hardware sector.
Open and Flexible Solutions
Further advancing its commitment to flexibility and open standards, Intel's Gaudi 3 emphasises open, community-based software and utilises industry-standard Ethernet networking to scale systems more effectively. This approach not only reduces dependencies on proprietary technologies but also aligns with Intel’s broader vision of democratizing AI technology. By promoting open solutions, Intel enables a wider range of businesses and developers to access cutting-edge AI capabilities, thus fostering a more inclusive and competitive environment.
Performance Benchmarks
Intel also highlights the performance benchmarks of Gaudi 3, positioning it as a superior option for both the training and inference phases of AI workloads. The accelerator is reported to be up to 50% faster in training tasks and offers a similar edge in inference throughput compared to NVIDIA’s H100 GPUs. These benchmarks not only showcase Gaudi 3’s technical superiority but also its capability to deliver more cost-effective and power-efficient solutions. Such performance metrics are crucial for businesses that rely on large-scale AI operations, as they translate directly into improved productivity and reduced operational costs.
Complementing the Gaudi 3 launch, Intel's broader AI strategy includes continuous innovation in AI chip technology and software development, spearheaded by leaders like Sandra Rivera. This holistic approach underlines Intel's vision for a diverse and competitive AI chip market poised for significant growth in the coming years.
Intel's Gaudi 3 AI accelerator represents a significant advancement in AI compute capabilities, offering a 4x increase in AI compute for BF16 and a 1.5x increase in memory bandwidth compared to its predecessor, Gaudi 2. This enhancement is crucial for handling the complex computations required by modern AI applications, including large language models and multimodal systems. The Gaudi 3's architecture, built on a 5nm process, also ensures greater energy efficiency and faster processing speeds, which are essential for sustainable, large-scale AI deployments.
How can the new chips help engineers move away from NVIDIA products?
The introduction of the Gaudi 3 accelerator by Intel is not just a significant milestone in its AI chip market journey but also reshapes the landscape of AI systems, offering a viable and potent alternative to existing platforms, particularly NVIDIA's.
Undoubtedly, the first implication that it could have is that engineers in the future may no longer be tied to NVIDIAs CUDA environment for AI acceleration. If Intel can offer its products at a competitive price, it could very well force NVIDIA to drop its prices, thereby creating a healthier chip market for AI applications.
Another potential change that Intel’s new chip range could introduce is the introduction of a new platform type, which will open up engineers to new software options. Considering that CUDA cores have been around for a number of years, they are not fully optimised for AI applications, whereas Intel’s new solution has been designed with AI from the ground up. As such, Intel platforms could offer better energy efficiency and higher processing speeds.
However, if the platform that Intel releases is fundamentally different to NVIDIA systems, it could potentially cause fragmentation in the AI market, making software hardware to port between NVIDIA and Intel hardware platforms. Such fragmentation can hinder the speed at which AI projects develop, thereby creating isolated development environments.
The introduction of the Gaudi 3 AI accelerator by Intel also includes significant improvements in networking capabilities, with support for industry-standard Ethernet networking. This feature allows for more flexible system scaling and reduces reliance on proprietary networking solutions, which have traditionally been a barrier to entry for smaller organisations. By providing an open, community-based software environment, Intel's Gaudi 3 enables a broader range of developers to innovate without the constraints imposed by vendor lock-in, fostering a more competitive and diverse AI development ecosystem.
As Intel continues to invest in software and hardware advancements, the future of AI chips looks promising. The competition between Intel and NVIDIA is expected to drive further innovation and technological advancements in the field of artificial intelligence computing. The launch of the Gaudi 3 chip signifies Intel's determination to challenge NVIDIA's dominance and establish itself as a key player in the evolving landscape of AI chip technologies.

