OCI Chiplet by Intel: High-Speed, Low-Power AI Infrastructure
Insights | 17-07-2024 | By Robin Mitchell
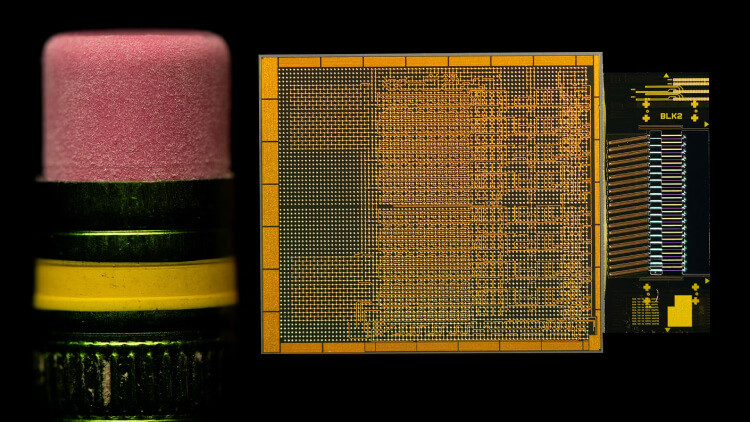
Intel has introduced a groundbreaking optical technology, the OCI chiplet, at the Optical Fiber Communication Conference 2024. This innovative chiplet supports bidirectional data transmission over longer distances with significantly reduced power consumption, catering to the escalating demands of AI infrastructure. With the potential to significantly enhance high-performance AI systems, Intel's OCI chiplet is a promising development in the tech industry.
What challenges do traditional electronic communication systems face compared to optical technologies, how does the OCI chiplet address the increasing bandwidth requirements of AI applications, and how might the adoption of this optical compute interconnect impact the future of AI infrastructure scalability?
Key Things to Know:
- Intel's OCI chiplet, unveiled at the Optical Fiber Communication Conference 2024, supports 64 channels of 32 Gbps data transmission, significantly enhancing AI infrastructure scalability.
- This innovative technology integrates Intel's silicon photonics, including on-chip lasers and optical amplifiers, offering high bandwidth, reduced power consumption, and extended reach.
- By addressing the critical needs of high-performance AI systems, the OCI chiplet reduces operational costs and environmental impact, promoting sustainable AI infrastructure development.
- Intel's OCI chiplet demonstrates robust performance in live data transmission over single-mode fiber, paving the way for future AI-driven computing platforms and applications.
The Unsustainable Future of Communication
As the world continues to rely on increasingly complex electronic networks for communication, it is evident that traditional electronic communication systems are facing a myriad of challenges that hinder their efficiency and sustainability. The reliance on copper traces for data transmission limits bandwidth, leading to slower data transfer rates that struggle to meet the demands of high-traffic environments such as data centres. Furthermore, the reliance on copper-based systems results in higher power consumption, escalating operational costs, and a larger environmental footprint, thus necessitating a shift towards more eco-friendly alternatives.
Another significant obstacle posed by traditional electronic systems is their limited distance capabilities. Signals degrade significantly over long distances, requiring repeaters or additional hardware to maintain signal integrity, a factor that complicates system design and scalability. Thus, these systems are typically designed with a specific range in mind, restricting their flexibility and adaptability in today's dynamic and evolving technological landscape.
Additionally, electronic systems are plagued by latency and interference issues, compromising signal integrity and causing data loss and communication disruptions. The susceptibility of these systems to electromagnetic interference (EMI) underscores the need for advanced shielding and filtering techniques to mitigate these challenges, adding complexity and cost to the design of electronic systems.
Overall, the limitations of traditional electronic communication systems present a significant hurdle in meeting the growing demands for efficient and sustainable communication technologies. As the need for high-speed, low-latency, and long-distance communication continues to escalate, the reliance on copper-based systems is unsustainable, necessitating the exploration of innovative solutions to optimise the future of communication.
The Future of AI Infrastructure Unveiled
In a significant milestone for the optical industry and AI computing, Intel recently showcased its Optical Compute Interconnect (OCI) chiplet at the Optical Fiber Communication Conference 2024. This innovative co-packaged device, developed by Intel's Integrated Photonics Solutions Group, marks a major advancement in optical technology for AI-driven infrastructure, paving the way for efficient, high-bandwidth communication in data centres and high-performance computing applications.
The OCI chiplet is a fully integrated optical compute interconnect co-packaged with an Intel CPU, supporting 64 channels of 32 Gbps data transmission in each direction over distances up to 100 meters using fiber optics. This technology is designed to meet the increasing demands for higher bandwidth, reduced power consumption, and extended reach, making it an essential addition to Intel's AI computing portfolio.
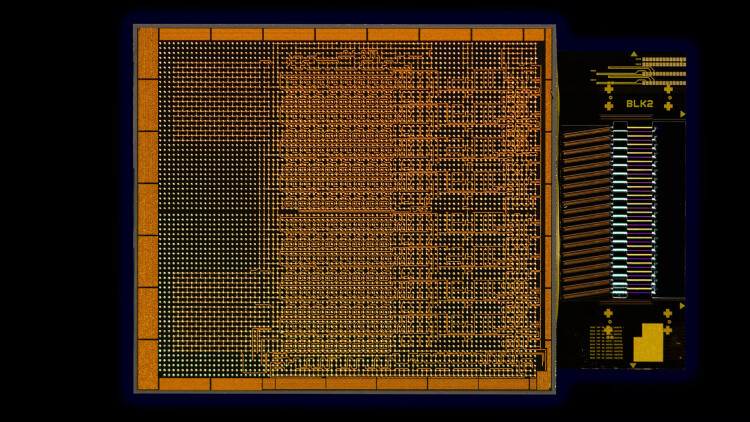
Intel’s Integrated Photonics Solutions Group has demonstrated the first fully integrated OCI chiplet co-packaged with an Intel CPU, running live data. This OCI chiplet supports optical I/O for emerging AI infrastructure in data centres and high-performance computing. (Credit: Intel Corporation)
Furthermore, the OCI chiplet's innovative design addresses the critical need for sustainable technology in AI infrastructure. By significantly reducing power consumption, it not only lowers operational costs but also minimises the environmental impact of large-scale data centers. This aligns with global efforts to promote eco-friendly technological advancements, ensuring that the growth of AI does not come at the expense of the planet.
Enhancing Efficiency and Scalability in AI Systems
With the ability to handle up to 4 Tbps bidirectional data transfer and compatibility with PCIe Gen5 standards, the OCI chiplet integrates Intel's silicon photonics technology, including on-chip lasers and optical amplifiers. The ability to co-package with various processors, such as CPUs, GPUs, IPUs, and other System-on-Chips (SoCs), makes the chiplet a versatile solution for enhancing the efficiency and scalability of AI computing systems.
The integration of Intel's silicon photonics technology within the OCI chiplet also enhances the reliability and durability of AI systems. The use of on-chip lasers and optical amplifiers ensures robust performance under various operational conditions, reducing the likelihood of system failures. This reliability is crucial for applications that require consistent, high-speed data processing, such as real-time AI analytics and large-scale machine learning operations.
During the OFC 2024 demonstration, Intel showcased a live optical link between two CPU platforms, showcasing the high signal quality and reliability of the OCI chiplet over a single-mode fiber. This demonstration highlights the chipset's potential to future-proof AI-driven computing platforms, addressing the needs of large language models and generative AI applications as they continue to advance.
This demonstration underscores the potential for Intel's OCI chiplet to transform AI infrastructure by providing a scalable and efficient solution for data-intensive applications. As AI models become more sophisticated, the demand for higher bandwidth and faster data processing will continue to grow. Intel's OCI chiplet is poised to meet these demands, offering a future-proof solution that can adapt to the evolving needs of AI technology.
A New Era of High-Speed Data Transmission
The Intel Optical Compute Interconnect chiplet represents a major advancement in high-speed data transmission, paving the way for enhanced AI infrastructure scalability and performance. By supporting 64 channels for high-speed data transmission, the OCI chiplet addresses the growing need for higher bandwidth, lower power consumption, and extended reach in AI systems, marking a significant shift from electrical to optical I/O in CPUs and GPUs.
The use of Intel's silicon photonics technology in the OCI chiplet enhances bandwidth, power efficiency, and latency, making it an essential component for future CPU/GPU cluster connectivity and innovative compute architectures like coherent memory expansion. The energy efficiency of the OCI chiplet promotes sustainable data centre operations, reducing energy costs and promoting environmentally friendly practices in high-performance computing environments. This cost-effective approach to optical interconnects will be crucial for the next generation of AI infrastructure, enabling advanced architectures and efficient system designs.
The integration of the OCI chiplet into Intel's hardware signifies a transformative change in computing, influencing network design and computational models. This game-changing technology is set to reshape high-performance computing and data centres, driving AI innovation forward. The future of AI infrastructure will rely on chiplets like the Intel Optical Compute Interconnect, which offers a high-speed, energy-efficient, and cost-effective solution for high-performance computing environments.

