Navigating Datasheets: Key Sections for Smarter Component Selection
25-02-2025 | By Mouser Electronics
This article was written by Vince Sosko, Technical Content Specialist at Mouser Electronics.
Datasheets are essential resources that influence purchasing choices, ensuring that engineers and designers select the right components for their applications. However, there is no universal format for datasheets—each manufacturer structures them differently, varying in detail, layout, and the type of information included. While these documents can be highly technical and dense, understanding their key sections can significantly streamline the decision-making process. Here’s a practical guide to help you efficiently navigate datasheets and determine whether a component suits your project or product.
Key Features of a Component
The Features section is usually positioned near the beginning of a datasheet, providing an overview of the component’s capabilities. This section often includes a bullet-point list that highlights critical attributes and performance benefits. For example, in the case of a microcontroller, you might see mentions of low power consumption, multiple input/output pins, high processing speed, or integrated analog-to-digital converters.
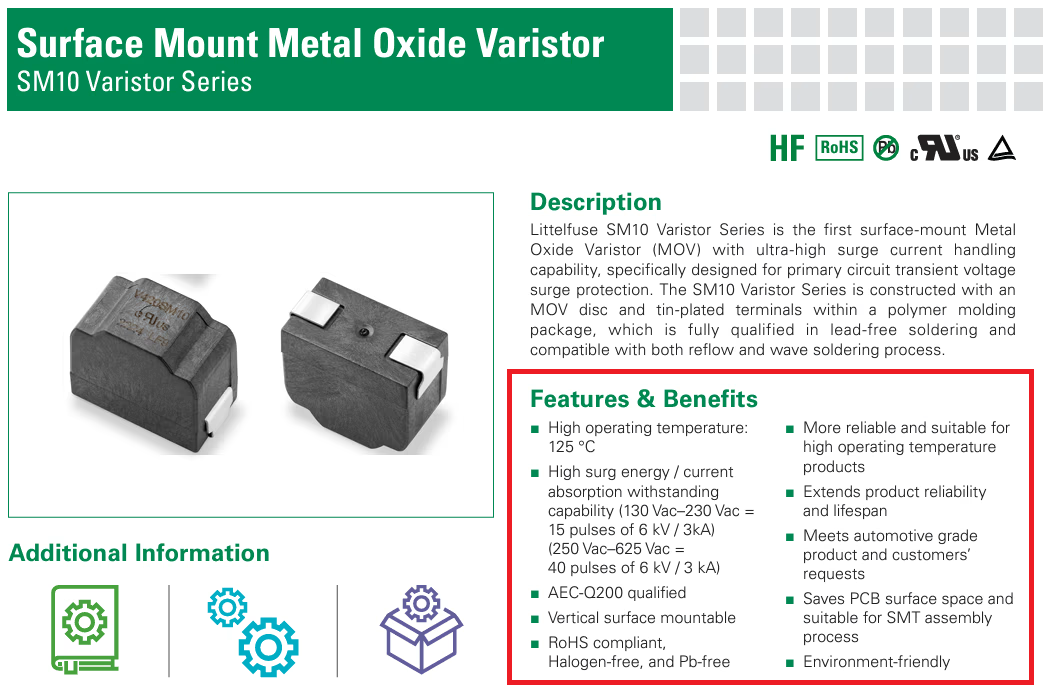
Understanding these features allows you to quickly evaluate whether a component aligns with your project’s requirements, such as power efficiency, operating voltage, and overall functionality.
Application Relevance
Adjacent to the features list, the Applications section outlines typical use cases for the component. This section provides context by listing common industries or product categories where the component is utilised. For instance, an operational amplifier may be suited for applications such as audio equipment, signal processing, instrumentation, or control systems.
Matching the component’s suggested applications to your specific project needs can help you refine your selection process, ensuring that the chosen component has a proven track record in similar environments.
Understanding Part Numbers
Deciphering part numbers can be challenging, yet they are crucial for ordering the correct components. Many datasheets include a breakdown of part numbers, explaining the logic behind the alphanumeric codes assigned to each variation. This helps identify specific details such as package type, temperature rating, and tolerance levels.
For example, a datasheet may present a part number from a family of wireless SoCs, detailing the attributes encoded within the number to help engineers and buyers select the correct variant. Some datasheets even provide a guide for constructing a part number, ensuring the chosen component meets all necessary specifications.
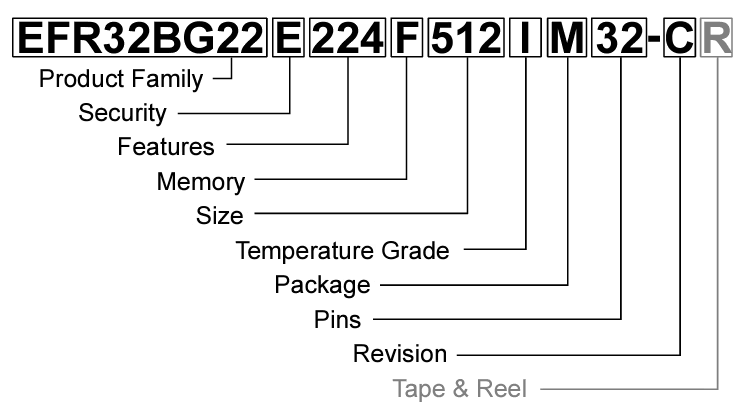
Since buyers typically focus on packaging considerations, it’s essential to confirm whether minor variations in a part number still align with the required specifications. Understanding how to interpret these numbers helps prevent ordering errors and delays in procurement.
Package Type Considerations
The Package Type section offers details about the component’s physical format, including drawings and precise dimensions. Selecting the correct package type ensures compatibility with a project’s footprint and assembly process. Common package types include:
- Dual in-line package (DIP): Ideal for through-hole mounting and easy handling.
- Small outline integrated circuit (SOIC): Designed for surface-mount applications with a compact layout.
- Quad flat package (QFP): Offers a high pin count suitable for advanced applications.
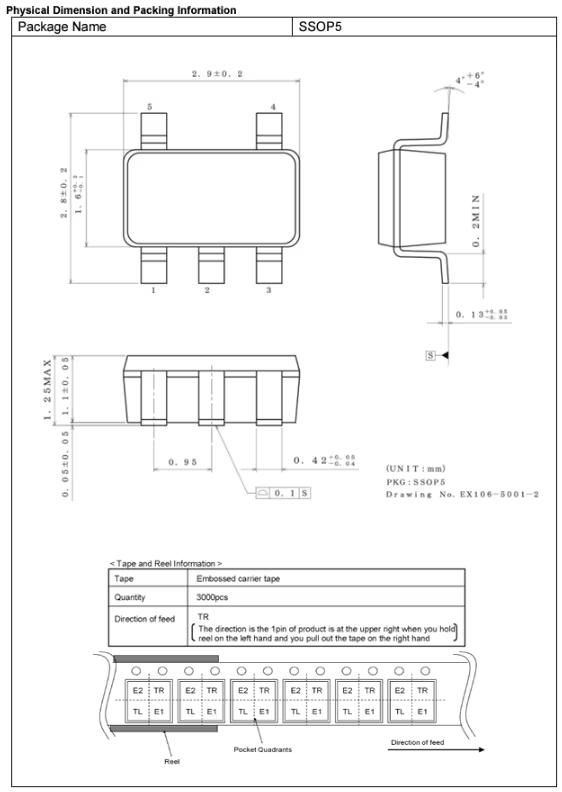
The chosen package type affects not only the assembly process but also the thermal performance and durability of the component in real-world conditions.
Technical Specifications to Consider
Beyond core features, applications, part numbers, and package types, datasheets include extensive technical details that may be more relevant to engineers than buyers. While some of this information may not be essential for procurement, having a basic understanding of these sections can be beneficial.
Electrical Characteristics
This section outlines key performance parameters, including:
- Operating Voltage: The acceptable voltage range for proper functionality.
- Current Consumption: The amount of current drawn in different states.
- Temperature Range: The operational limits in varying environmental conditions.
These specifications help ensure that a component performs reliably under the intended operating conditions. Paying close attention to maximum ratings can prevent overstressing and potential failures.
Performance Data
Many datasheets include graphs and charts that illustrate how a component behaves under different conditions, such as power dissipation versus ambient temperature or efficiency curves. These visual aids offer insights into real-world performance.
Pin Configuration and Functionality
A pin configuration diagram provides a visual representation of the component’s pins or leads. It is accompanied by a functional description that explains the role of each pin—such as power supply, ground, input/output, and control signals—ensuring seamless integration into a circuit design.
Mechanical Dimensions
Manufacturers typically provide detailed mechanical dimensions to ensure proper placement on printed circuit boards (PCBs) and within enclosures.
Making an Informed Choice
Interpreting datasheets accurately is an important skill for anyone involved in electronics design and procurement. By focusing on key elements such as features, applications, part number details, and package types, you can make confident and well-informed purchasing decisions.
While datasheets can be dense, breaking them down into relevant sections simplifies the process, making it easier to extract the necessary information. Some distributors also offer technical support services to help navigate complex datasheets, ensuring you select the right components for your project.

